Circular economy for plastics
Biotechnological solutions for degradation and recycling of plastics
Advertisement
plastics are wonderful materials. They are extremely versatile and of almost eternal durability. But that also causes a problem. After around 100 years of plastic production, plastic particles are almost everywhere: in ground water, the oceans, the air and the food chain. Across the globe, considerable efforts are being taken to solve this “plastic crisis” by using biotechnological methods. However, most progress is restricted to a specific type of plastic, namely polyesters such as PET. A comment in the journal Nature Catalysis critically discusses the state of current research and suggests strategies for a bio-based circular economy for plastics.
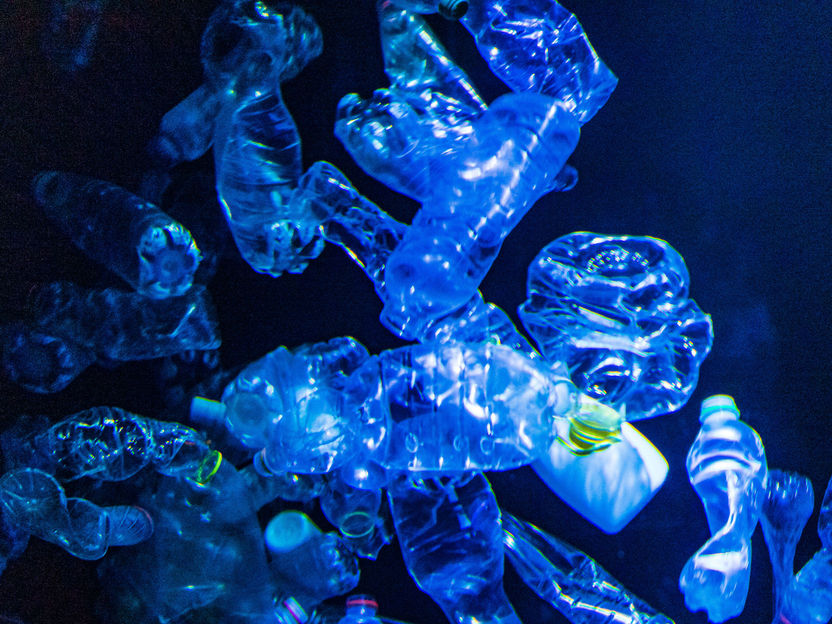

Plastic in the sea
Jan Meßerschmidt
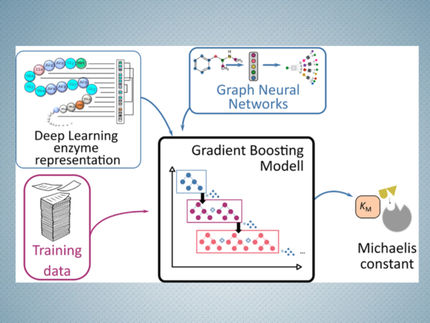
Sophisticated solutions are required to achieve a circular economy for plastics. Currently, only a fraction of the plastic materials are recycled using energy and cost-intensive processes. One possibility for degrading certain plastics into their building blocks is to use enzymes or biotechnological processes that make use of microorganisms. The building blocks that are released, also called monomers, can be used to make new plastics. If it is not possible to directly re-use the building blocks, the plastic should be degraded as far as possible to relieve the environment and provide access to the raw materials. Modern biotechnology can make a substantial contribution to both the end-of-use recycling of plastics as well as the aim to achieve a carbon neutral balance.
The publication “Possibilities and limitations of biotechnological plastic degradation and recycling” jointly written by scientists from the University of Greifswald, RWTH Aachen, the Fraunhofer Institut UMSICHT and University College Dublin, discusses the state of current research and highlights strategies for future developments. The authors are contributing towards the joint project MIX-UP – funded by the European Union in the framework of Horizon 2020 – together with scientists from China, to try to find ways of creating value from plastic waste originating from oceans as well as households, by using biotechnological methods. In these processes, microorganisms use the degradation products from plastics in a so-called “up-cycling” as a source of carbon for making valuable products.
“Whilst highly efficient enzymes have already been discovered and improved for the widely used plastic polyethylene terephthalate (PET), thus enabling economical recycling, no significant progress has yet been made for most other plastics,” explains Prof. Uwe Bornscheuer from the University of Greifswald. Dr. Ren Wei, who leads a junior research group at the Institute of Biochemistry adds that: “Unfortunately, there are several publications that raise false hopes. For instance, there is a lack of solid scientific proof in some reports about plastic-eating insects.”
Prof. Lars Blank from RWTH Aachen emphasises: “We need to distinguish two aspects: plastics, which we deliberately expose to the environment, such as mulching foils for agriculture, need to be decomposed rapidly – within weeks or months. For durable plastics, we need a medium-term solution. It should be ensured that degradation will take place within a few years – instead of centuries as is the case at the moment.” The authors suggest a scenario based on the following six principles: rethink – refuse – reduce – reuse – recycle – replace. They also aim to initiate a lively discussion on how to achieve a circular economy for plastics in the near future.