Magnetized viruses attack harmful bacteria
Advertisement
Magnetic nanoparticle clusters have the power to punch through biofilms to reach bacteria that can foul water treatment systems, according to scientists at Rice University and the University of Science and Technology of China.
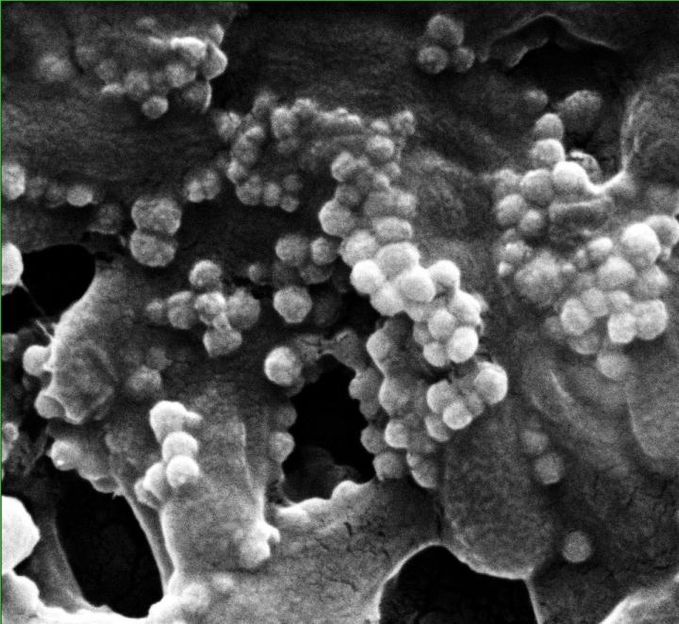
Bacteriophages combined with nanoparticle clusters can be drawn into a biofilm with a magnet. Researchers at Rice University and the University of Science and Technology of China developed the material to kill hard-to-reach bacteria protected by biofilms in water treatment systems.
Alvarez Group/Rice University
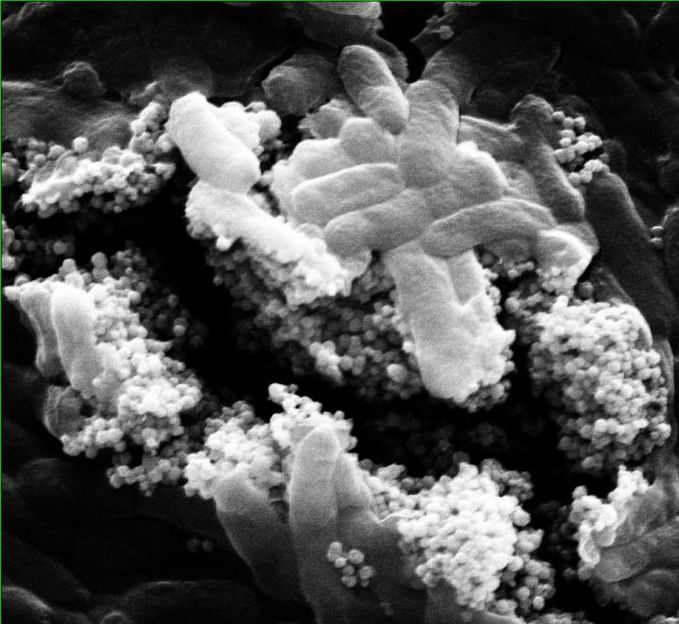
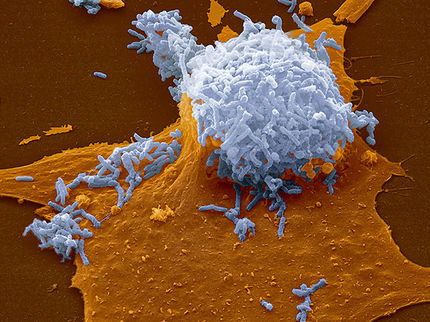
Clusters of nanoparticles with phage viruses attached find and kill Escherichia coli bacteria in a lab test at Rice University. Researchers at Rice and the University of Science and Technology of China have developed a combination of antibacterial phages and magnetic nanoparticle clusters that infect and destroy bacteria that are usually protected by biofilms in water treatment systems.
Alvarez Group/Rice University
The nanoclusters developed through Rice's Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment (NEWT) Engineering Research Center carry bacteriophages -- viruses that infect and propagate in bacteria -- and deliver them to targets that generally resist chemical disinfection.
Without the pull of a magnetic host, these "phages" disperse in solution, largely fail to penetrate biofilms and allow bacteria to grow in solution and even corrode metal, a costly problem for water distribution systems.
The Rice lab of environmental engineer Pedro Alvarez and colleagues in China developed and tested clusters that immobilize the phages. A weak magnetic field draws them into biofilms to their targets.
"This novel approach, which arises from the convergence of nanotechnology and virology, has a great potential to treat difficult-to-eradicate biofilms in an effective manner that does not generate harmful disinfection byproducts," Alvarez said.
Biofilms can be beneficial in some wastewater treatment or industrial fermentation reactors owing to their enhanced reaction rates and resistance to exogenous stresses, said Rice graduate student and co-lead author Pingfeng Yu. "However, biofilms can be very harmful in water distribution and storage systems since they can shelter pathogenic microorganisms that pose significant public health concerns and may also contribute to corrosion and associated economic losses," he said.
The lab used phages that are polyvalent -- able to attack more than one type of bacteria -- to target lab-grown films that contained strains of Escherichia coli associated with infectious diseases and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is prone to antibiotic resistance.
The phages were combined with nanoclusters of carbon, sulfur and iron oxide that were further modified with amino groups. The amino coating prompted the phages to bond with the clusters head-first, which left their infectious tails exposed and able to infect bacteria.
The researchers used a relatively weak magnetic field to push the nanoclusters into the film and disrupt it. Images showed they effectively killed E. coli and P. aeruginosa over around 90 percent of the film in a test 96-well plate versus less than 40 percent in a plate with phages alone.
The researchers noted bacteria may still develop resistance to phages, but the ability to quickly disrupt biofilms would make that more difficult. Alvarez said the lab is working on phage "cocktails" that would combine multiple types of phages and/or antibiotics with the particles to inhibit resistance.